Headless Browser
HeadlessChrome: What Is It and How to Detect It?
What is Headless Chrome? What can headless browser be used for? How to detect and anti-detect headless browsers? All these questions you will find answers in this article.
May 22, 2024Robin Brown
A headlesschrome is a type of browser that lacks a graphical user interface (GUI). It can run in the background, allowing programmers to control and manipulate the browser through a command-line interface or scripts.
Now, it's time to learn about the methods of detecting and anti-detecting headless browser crawler bots through Nstbrowser!
What is Headlesschrome?
Headlesschrome is a headless mode of the Google Chrome browser. It allows developers to control and manipulate the Chrome browser via command line or scripts without displaying the browser's user interface. Headlesschrome combines the powerful features of the Chrome browser with the efficiency of headless mode, making it an indispensable tool in modern web development and testing.
What Can a Headlesschrome Do?
- Efficient Automated Testing: Headless browsers can quickly run browser test scripts to verify the functionality, performance, and compatibility of web pages without loading and rendering the user interface, greatly improving testing speed and efficiency.
- Web Scraping: A headlesschrome can be used for scraping web content, simulating user operations to access and extract data from dynamic web pages. This is especially useful for handling pages that require login, load dynamic content, or rely on JavaScript-generated content.
- Performance Monitoring: Developers can use headless browsers to monitor and analyze web page performance, such as load times and resource usage.
Ready to learn more and get special benefits?
Join our Discord referral program to share $1,500 in cash now!
How to Detect and Anti-Detect Headlesschrome?
We already know what a headlesschrome is, what it can do, and how it works. Since headless browsers have strong automation features, headless browsers are also often used for anti-crawling purposes. Therefore, detecting their presence is crucial.
Here are common methods of detecting headless browsers with JavaScript code examples and some anti-detection methods:
1. User Agent Detection
The user agent is the identifier sent by the browser to the server. By checking whether the user agent contains the word "Headless", we can initially determine whether the request is from a headless browser. This method is often unreliable because the user agent can be forged or modified.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isHeadlessUserAgent = navigator.userAgent.toLowerCase().includes('headless');- Anti-Detection Code
javascript
// custom userAgent without 'headless'
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'userAgent', {
value: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/124.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
});2. JavaScript Execution Detection
Headlesschrome usually does not execute JavaScript or their JavaScript execution capabilities are weak. Therefore, we can determine whether the browser supports JavaScript by executing some simple JavaScript code. This can be achieved by checking the availability of certain JavaScript APIs or features.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isJavaScriptEnabled = typeof window !== 'undefined';3. Browser Feature Detection
Certain browser features may be disabled or behave abnormally in a headlesschrome. We can use these features for detection. For example, the Canvas API can be used to detect headless browsers.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isCanvasSupported = () => {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const context = canvas.getContext('2d');
return !!context;
}4. WebDriver Detection
By checking the existence of the navigator.webdriver property, we can determine whether it is a headlesschrome. Headless browsers usually set this property, whereas normal browsers do not. The relevant source code can be found in Chromium. By checking the presence of this property, we can determine if it is a headlesschrome.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isWebDriverSupported = () => {
return navigator.webdriver;
}- Anti-Detection Code
javascript
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'webdriver', {
get: () => undefined
});5. window.chrome Detection
Detecting whether window.chrome exists can help determine if the browser is in headless mode. In headless mode, this property is usually absent.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isWindowChromeSupported = () => {
return window.chrome !== undefined;
}6. WebRTC Detection
WebRTC is a web standard for real-time communication in browsers. Details can be found on the Webrtc website. Headlesschrome usually disables WebRTC, so we can determine if the browser is headless by checking WebRTC availability.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isWebRTCSupported = () => {
return !!window.RTCPeerConnection;
}7. Audio/Video Detection
In headless mode, playing audio or video is usually disabled. By attempting to play audio or video, we can determine if the browser supports audio or video playback and thus if it is a headlesschrome.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isAudioVideoSupported = () => {
const audio = document.createElement('audio');
const video = document.createElement('video');
return !!(audio.canPlayType && video.canPlayType);
}8. Headless Permission Detection
Currently, headless browsers cannot operate browser permissions, so they do not support Notification.permission. Because they do not handle user interface events, they only load and render pages. Therefore, in headlesschrome mode, Notification.permission and navigator.permissions.query are inconsistent.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isHeadlessPermissionMatched = () => {
return navigator.permissions.query({name: 'notifications'})
.then(permissionStatus => {
return Notification.permission === 'denied' && permissionStatus.state === 'prompt';
})
.catch(() => {
return false;
});
};9. navigator.plugins Detection
navigator.plugins can be used to check the list of plugins present in the browser. By default, browsers install some plugins like Chrome PDF viewer or Google Native Client, but in headless mode, there are usually no plugins. Therefore, we can determine if it is a headlesschrome by checking if the plugin list is empty.
- Detection Code
javascript
const pluginInstalled = () => {
return navigator.plugins.length > 0
}- Anti-Detection Code
javascript
const originalPlugins = navigator.plugins;
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'plugins', {
get: () => originalPlugins
});10. Language Detection
In Chrome, navigator.language and navigator.languages can be used to get the user's language. The first one is the language of the browser UI, and the second one is the list of user preferred languages. In headless mode, navigator.languages returns an empty string.
- Detection Code
javascript
const isHeadlessLanguage = () => {
return !navigator.languages || navigator.languages.length === 0
}- Anti-Detection Code
javascript
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'languages', {
value: ['en-US', 'en']
});11. Other Common Methods
Detection Methods:
- Page Load Speed Detection: Headlesschrome usually loads pages faster because they do not need to render the page or execute JavaScript. We can determine if it is a headless browser by monitoring the page load speed.
- Keyboard Event Detection: Headless browsers usually do not trigger keyboard events because they do not need to interact with users. We can determine if it is a headlesschrome by listening for keyboard events and checking if they are triggered.
- Mouse Event Detection: Similarly, headless browsers do not trigger mouse events because they do not need to simulate user operations. We can detect if it is a headlesschrome by listening to mouse events.
- CSS Detection: Certain CSS styles may behave differently in headless browsers. For example, some CSS properties may not be supported or render differently. We can determine if it is a headlesschrome by loading specific CSS styles and checking the rendering results.
- LocalStorage Detection: Headless browsers usually do not support LocalStorage because they do not need to maintain user sessions or states. We can determine if it is a headlesschrome by attempting to read or write LocalStorage and checking if it succeeds.
Anti-detection methods
- Simulate human behavior: Headless browsers usually perform tasks in a highly automated manner, such as page loading, form submission, etc., which is different from the behavior patterns of human users. Human behavior can be simulated, such as adding random mouse movements, keyboard input, etc., to make the detector think that it is a real user operation rather than a headlesschrome.
- Randomize request intervals: Headless browsers usually send requests at a very regular frequency. The behavior of real users can be simulated by adding random time intervals between requests, which makes it difficult for the detector to determine whether it is a headlesschrome by the request frequency.
- Simulate browser environment: Modify some properties or functions in the headless browser to make it more like a real browser. For example, the browser window size, display resolution, User-Agent, etc. can be modified to simulate the environment of a real browser.
- Embed JavaScript interaction: Headless Chromes usually do not execute a lot of JavaScript code or interact with the page. You can embed some JavaScript code that requires user interaction in the page and detect its execution results to determine whether it is a headlesschrome.
- Detect specific environment variables: Headless browsers usually set some specific environment variables or properties, which can be detected to determine whether it is a headlesschrome. For example, you can detect whether a specific identifier exists in the environment variable, or detect whether a specific global variable exists in JavaScript.
It should be noted that because headless browsers can simulate the behavior of almost all normal browsers, they will use various anti-detection methods to make headless browsers look more like real users, thereby increasing the difficulty of anti-crawling. Therefore, no matter what method is used to anti-detect headless browsers, it is not absolutely reliable, at least so far.
Anti-headlesschrome Detection Using Fingerprint Browsers
We can also use fingerprint browsers to bypass headlesschrome detection. Let's take Nstbrowser fingerprint browser as an example. Nstbrowser's API solution is currently one of the best choices to avoid robot detection, and you can get the API key for free.
Why use Nstbrowser for detection?
- Nstbrowser is completely free to use
- Nstbrowserless is compatible with popular Puppeteer and Playwright, providing more comprehensive technical support
- It supports starting the browser in headless mode through the API
Next, visit the CreepJS and Areyouheadless headlesschrome detection sites through the Nstbrowser fingerprint browser and my local GoogleChrome browser to compare the headless browser detection effect.
We will use Puppeteer to call the API to start the headless fingerprint browser. Specifically, the LaunchExistBrowser interface will be used. Of course, you can also choose other APIs you need according to the document.
Before you start, you need to:
-
Step 1. Download and install Nstbrowser in advance
-
Step 2. Generate API Key
-
Step 3. Create a Profile and manually download the kernel. You can also click on the client to start your Profile and then trigger the automatic download of the kernel
After everything is ready, you can start coding. The following code shows how to start the headless mode browser and visit the headless browser detection site and take a screenshot:
javascript
import puppeteer from 'puppeteer-core';
// wiat for millseconds
function sleep(millseconds) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, millseconds));
}
// visit headless detection site and take screenshots
async function execPuppeteer(browserWSEndpoint) {
try {
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: browserWSEndpoint,
defaultViewport: null,
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
// detect headless on creepjs site
await page.goto('https://abrahamjuliot.github.io/creepjs');
await sleep(5 * 1000);
await page.screenshot({ fullPage: true, path: 'detect_headless_creepjs.png' });
// detect headless on areyouheadless site
await page.goto('https://arh.antoinevastel.com/bots/areyouheadless');
await sleep(2 * 1000);
await page.screenshot({ path: 'detect_headless_areyouheadless.png' });
await page.close();
await browser.disconnect();
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
}
// LaunchExistBrowser: Connect to or start an existing browser
// You need to create the corresponding profile in advance
// Support custom config
async function launchAndConnectToBrowser(profileId) {
const host = 'localhost:8848';
const apiKey = 'you api key;
const config = {
headless: true, // support: true, 'new'
autoClose: true,
};
const query = new URLSearchParams({
'x-api-key': apiKey, // required
config: encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify((config))),
});
const browserWSEndpoint = `ws://${host}/devtool/launch/${profileId}?${query.toString()}`;
console.log('browserWSEndpoint: ', browserWSEndpoint);
await execPuppeteer(browserWSEndpoint);
}
launchAndConnectToBrowser('your profile id').then();Running results:
CreepJS test results
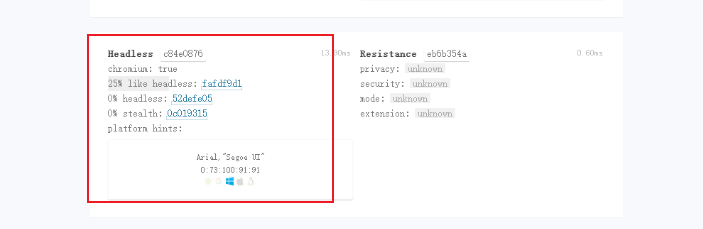
Areyouheadless test results
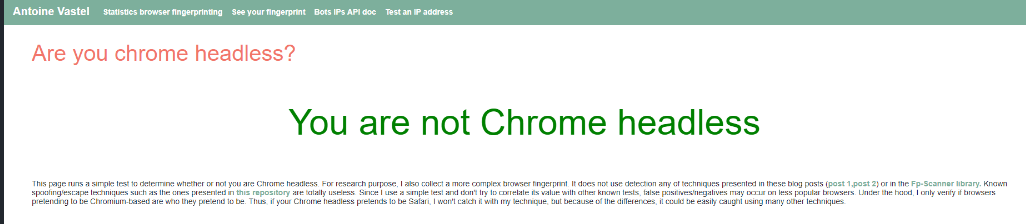
By comparing the running result screenshots with the detection results of my local Google Chrome, I found that the headless detection of these two sites did not recognize that we were using a headlesschrome, which is also the effect we want.
The Bottom Line
Through the discussion and sample code of this article, we hope to provide developers with effective reference and guidance to improve the security and data protection capabilities of the website.
Detection and anti-detection of a headlesschrome is an evolving technical confrontation process. You can use effective anti-detection tools to deal with the risk of being detected and blocked. Nstbrowser can help you ensure absolute concealment and use advanced technology to unlock network blockades.
In addition, developers need to continue to pay attention to the latest technical developments and update detection strategies to meet new challenges. No matter what method is used to anti-detect headless browsers, it needs to be continuously optimized and improved to ensure its effectiveness and reliability.
More






