Browserless
How to do Web Scraping with Browserless in the Cloud?
Unlock the power of cloud browsers! Discover why Browserless is your go-to for seamless web scraping and learn how to get started in the cloud!
Sep 24, 2024Robin Brown
What Are Cloud Browsers?
Cloud Browser is a cloud-based combination of a web browser application with a virtualized container that implements the concept of remote browser isolation. Developers can automate web browsers using popular tools such as Playwright and Puppeteer for web scraping and web testing.
Cloud Browser executes commands from the network in a secure container, separate from the user endpoint, and accessed through a remote display protocol. As a result, browser applications are more centralized, easier to manage, more cost-effective, scalable, and protected.
Why Scrape With Browserless?
Browserless is a powerful cloud-based solution for seamless browser automation, web scraping, and testing. The primary goal of Browserless is to simplify and scale up web browser automation tasks like testing and scraping and this can be approached in one of two ways:
- Running multiple browser instances on Docker or Kubernetes.
- Using existing Web Driver proxy servers like Selenium Grid.
How to do web scraping with Browserless in the Cloud?
Step1: Preparation
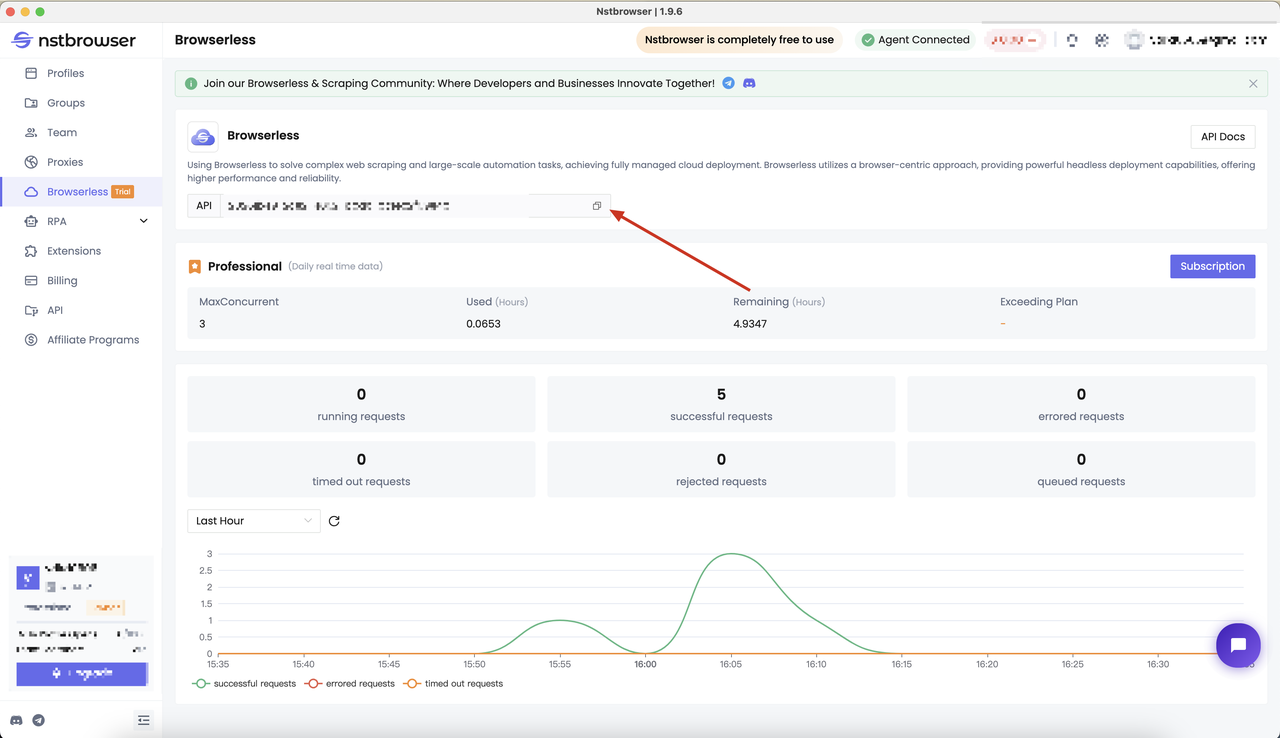
Before we start, we need to have a Browserless service. Using Browserless can solve complex web crawling and large-scale automation tasks, and it has now achieved fully managed cloud deployment.
Browserless adopts a browser-centric approach, provides powerful headless deployment capabilities, and provides higher performance and reliability. For more information about Browserless, you can get the document to learn more.
- Get the API KEY and go to the Browserless menu page of the Nstbrowser client, or you can go to the Nstbrowser client to access
Do you have any wonderful ideas and doubts about web scraping and Browserless?
Let's see what other developers are sharing on Discord and Telegram!
Step2: Confirm crawling target
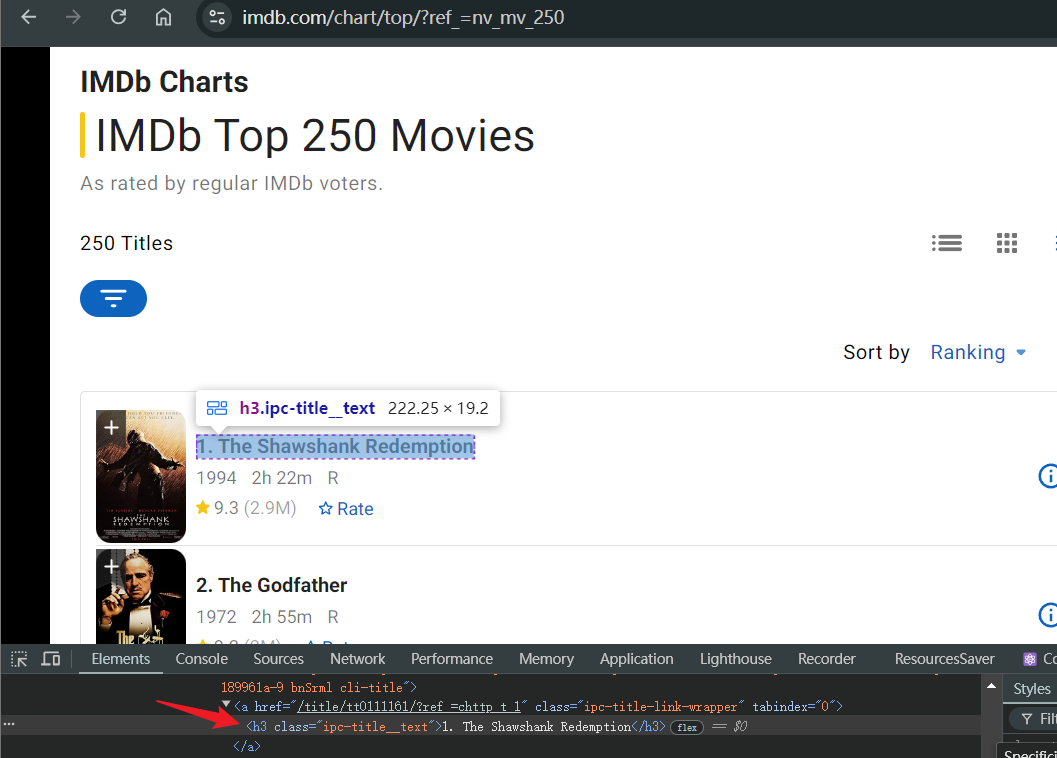
Before we start, we need to make sure what we are going to crawl. In the following example, we try to crawl the movie titles in IMDb's Top 250 Movies. After opening the page:
- Wait for the page to load normally and locate the page to the movie title under IMDb Top 250 Movies
- Open the debug console and identify the html element of the movie title
- Use your favorite library to get the movie title
Step3: Start crawling
Everything is ready, start crawling! We choose to use the powerful Cloud Browserless provided by Nstbrowser to crawl the above content. Below we will list some of the common libraries used together.
Puppeteer
If you haven't chosen a library yet, we highly recommend Puppeteer because it is very active and has many maintainers. It is also built by Chrome developers, so it is one of the highest-quality libraries.
- Install puppeteer-core
Bash
# pnpm
pnpm i puppeteer-core
# yarn
yarn add puppeteer-core
# npm
npm i --save puppeteer-core- Code script
JavaScript
import puppeteer from "puppeteer-core";
const token = "your api key"; // 'your proxy'
const config = {
proxy: 'your proxy', // required; input format: schema://user:password@host:port eg: http://user:password@localhost:8080
// platform: 'windows', // support: windows, mac, linux
// kernel: 'chromium', // only support: chromium
// kernelMilestone: '128', // support: 128
// args: {
// "--proxy-bypass-list": "detect.nstbrowser.io"
// }, // browser args
// fingerprint: {
// userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/128.0.6613.85 Safari/537.36', // userAgent supportted since v0.15.0
// },
};
const query = new URLSearchParams({
token: token, // required
config: JSON.stringify(config),
});
const browserWSEndpoint = `https://less.nstbrowser.io/connect?${query.toString()}`;
// Connect browserless
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint,
defaultViewport: null,
})
console.info('Connected!');
// Create new page
const page = await browser.newPage()
// Visit IMDb top 250 page
await page.goto('https://www.imdb.com/chart/top/?ref_=nv_mv_250')
// Wait for the movie list to load
await page.waitForSelector('.ipc-metadata-list')
// Get a list of movie titles
const moviesList = await page.$$eval('.ipc-metadata-list h3.ipc-title__text', nodes => nodes.map(node => node.textContent));
console.log('[IMDb Top 250 Movies]===>', moviesList);
// Close browser
await browser.close();Congratulation! We have finished our scraping task. You can see the result of 250 movies in the console:

Playwright
It is an active open-source project with a large number of contributors. Playwright was developed by Microsoft and supports multiple browsers (Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit) and multiple programming languages (Nodejs, Python, .NET, and Java), making it one of the most versatile and high-quality browser automation tools.
Use in Nodejs
- Install Playwright
Bash
# pnpm
pnpm create playwright
# yarn
yarn create playwright
# npm
npm init playwright@latest- Code script
JavaScript
import { chromium } from 'playwright'
const token = "your api key"; // 'your proxy'
const config = {
proxy: 'your proxy', // required; input format: schema://user:password@host:port eg: http://user:password@localhost:8080
// platform: 'windows', // support: windows, mac, linux
// kernel: 'chromium', // only support: chromium
// kernelMilestone: '128', // support: 128
// args: {
// "--proxy-bypass-list": "detect.nstbrowser.io"
// }, // browser args
// fingerprint: {
// userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/128.0.6613.85 Safari/537.36', // userAgent supportted since v0.15.0
// },
};
const query = new URLSearchParams({
token: token, // required
config: JSON.stringify(config),
});
const browserWSEndpoint = `ws://less.nstbrowser.io/connect?${query.toString()}`;
// Connect browserless
const browser = await chromium.connectOverCDP(browserWSEndpoint);
console.info('Connected!');
// Create new page
const page = await browser.newPage();
// Visit IMDb's top 250 page
await page.goto('https://www.imdb.com/chart/top/?ref_=nv_mv_250');
// Wait for movie list to load
await page.waitForSelector('.ipc-metadata-list');
// Get a list of movie titles
const moviesList = await page.$$eval('.ipc-metadata-list h3.ipc-title__text', nodes => nodes.map(node => node.textContent));
console.log('[IMDb Top 250 Movies]===>', moviesList);
// Close browser
await browser.close();Here we can figure out the lists after running our project:

Use in Python
- Install Playwright
Bash
pip install pytest-playwright- Code script
Python
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
from urllib.parse import urlencode
import json
token = "your api key" # 'your proxy'
config = {
"proxy": "your proxy", # required; input format: schema://user:password@host:port eg: http://user:password@localhost:8080
# platform: 'windows', // support: windows, mac, linux
# kernel: 'chromium', // only support: chromium
# kernelMilestone: '128', // support: 128
# args: {
# "--proxy-bypass-list": "detect.nstbrowser.io"
# }, // browser args
# fingerprint: {
# userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/128.0.6613.85 Safari/537.36', // userAgent supportted since v0.15.0
# },
}
query = urlencode({"token": token, "config": json.dumps(config)})
browser_ws_endpoint = f"ws://less.nstbrowser.io/connect?{query}"
def scrape_imdb_top_250():
with sync_playwright() as p:
# Connect browserless
browser = p.chromium.connect_over_cdp(browser_ws_endpoint)
print("Connected!")
# Create new page
page = browser.new_page()
# Visit IMDb top 250 page
page.goto("https://www.imdb.com/chart/top/?ref_=nv_mv_250")
# Wait for movie list to load
page.wait_for_selector(".ipc-metadata-list")
# Get a list of movie titles
movies_list = page.eval_on_selector_all(
".ipc-metadata-list h3.ipc-title__text",
"nodes => nodes.map(node => node.textContent)",
)
print("[IMDb Top 250 Movies]===>", movies_list)
# Close browser
browser.close()
scrape_imdb_top_250()Of course, the following is the scraping result:

Select your favorite language and library, execute the corresponding script, and you can see the crawled results!
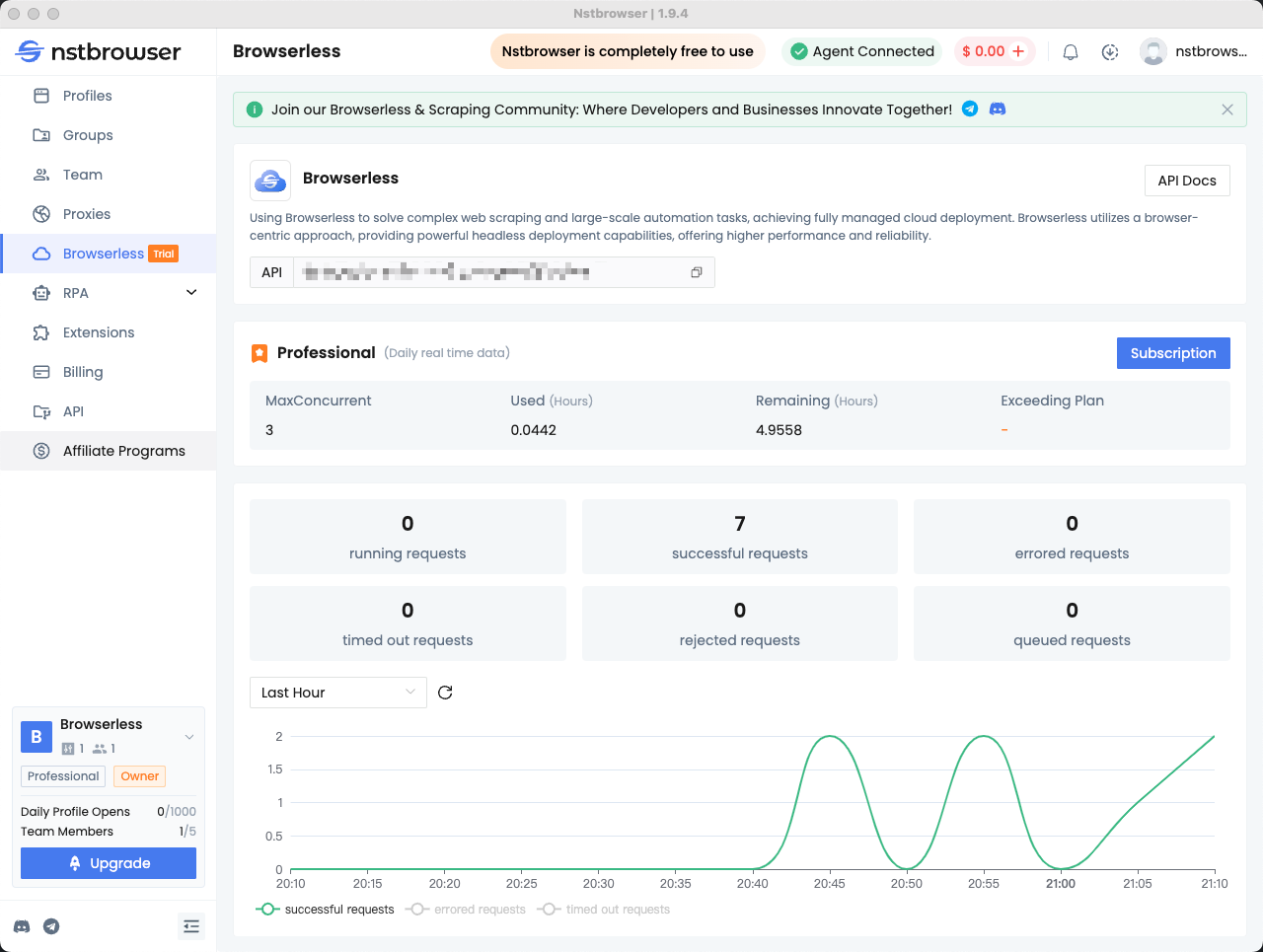
Step4: View the Browserless Dashboard
You can view all statistics for recent requests and remaining session time in the Browserless menu of the Nstbrowser client.
5 Tips to Bypass Scraper Blocking with Browserless?
There are some key differences between headless browsers and regular browsers. The anti-bot service detects headless browsers by spotting these differences.
Bypassing scraper blocking with Browserless involves several key strategies:
- Use Headless Browsers: Browserless allows you to run headless browsers like Puppeteer, which can mimic real user behavior and reduce detection risks.
- Rotate User Agents: Randomizing user agents can help avoid blocking by making your requests appear to come from different browsers.
- Implement Proxy Rotation: Utilize rotating proxies to change IP addresses frequently, minimizing the chances of being blocked by target websites.
- Throttle Requests: Mimic human-like browsing behavior by introducing delays between requests, preventing rapid-fire requests that trigger security measures.
- Manage Cookies and Sessions: Properly handle cookies and session data to maintain continuity and avoid detection, as persistent sessions are less likely to be flagged.
What are the differences Between Browserless and Headless Browser?
- Definition:
Browserless: A service or platform that provides cloud-based browser automation, enabling users to run headless browsers without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Headless Browser: A web browser without a graphical user interface (GUI) that can be run in a command-line environment, useful for automating web tasks.
- Management:
Browserless: Offers managed services, abstracting the complexity of setting up and maintaining browser instances. Users interact with an API to initiate tasks.
Headless Browser: Requires users to set up and manage the browser environment, including dependencies and configurations.
- Scalability:
Browserless: Designed for scalability, allowing users to run multiple browser instances in parallel easily, leveraging cloud resources.
Headless Browser: Scaling may involve more manual work, such as managing multiple instances and server resources.
- Use Cases:
Browserless: Ideal for developers and teams needing scalable automation for web scraping, testing, and data extraction without infrastructure concerns.
Headless Browser: Suitable for developers who prefer direct control over their automation tasks and are comfortable managing their own environment.
- Integration:
Browserless: Often provides integrations with various tools and services, making it easier to incorporate into existing workflows.
Headless Browser: Requires custom integration efforts to connect with other tools or services.
It's a Wrap
How to do web scraping with browserless in the Cloud? We have already explored 4 detailed steps. Just choose your favorite library and then scrape the data you need.
In addition, we have also learned that:
- What is a Cloud browser?
- Benefits of Browserless
- 5 effective to avoid blocking
Start using Browserless to simplify everything!
More






