Browserless
What Is HTTP/2 Fingerprinting and How to Bypass It?
Learn how to bypass HTTP/2 fingerprinting in web scraping with six powerful methods, from using real browsers to cloud-based Browserless. Stay undetected against modern anti-bot defenses.
Jun 03, 2025Carlos Rivera
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape of web scraping and anti-scraping technologies, traditional techniques such as User-Agent spoofing and JavaScript bypass are no longer sufficient to deal with increasingly sophisticated detection mechanisms. As more websites migrate to the efficient HTTP/2 protocol, HTTP/2 fingerprinting has quietly emerged as a powerful anti-scraping weapon.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What HTTP/2 is and how it works
- Six practical methods to bypass HTTP/2 fingerprinting
Follow my words and figure out more!
What is HTTP/2?
HTTP/2 is the second generation of the HTTP protocol. Since its release in 2015, approximately half of all websites have adopted it. For example:
- Google (including Gmail, Search, Drive, etc.)
- YouTube
- Amazon
- Netflix
You can check whether a request uses HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2 (h2) by pressing F12 in your browser and looking at the Network tab.
HTTP/2 improves page load performance through multiplexing, header compression (HPACK), and connection reuse. Unlike the serial nature of HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2 handles multiple requests and responses concurrently over a single connection.
Key features include:
- Multiplexing: Multiple requests share one TCP connection
- Header compression: Uses HPACK to reduce redundancy
- Binary protocol: More efficient structure for data transmission
- Priority control: Optimizes resource scheduling
What is HTTP/2 Fingerprinting?
HTTP/2 fingerprinting is a technique that identifies clients by analyzing subtle differences in their behavior when using the HTTP/2 protocol. These differences often lie in how the protocol is implemented. Different browsers, scraping libraries, and automation tools expose unique characteristics at a low level.
In simple terms:
Instead of identifying you through your User-Agent, it observes how your client behaves at the HTTP/2 layer to determine whether you’re a "script pretending to be a browser."
HTTP/2 transmits binary frames that include various fields.
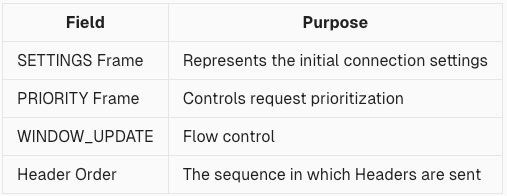
Each client implements these frames—values, order, combinations—differently. Anti-scraping systems build fingerprint databases based on this to identify:
- Whether you're using Python’s
requests + httpx - Whether you’re using Playwright + Node.js
- Whether you're a real Chrome browser user
You can view your own HTTP/2 fingerprint on BrowserLeaks' HTTP/2 test page.
Common fingerprint indicators include:
- SETTINGS content: Each client sets different parameters
- HEADERS order: The sequence of :method, :path, user-agent, etc.
- PRIORITY frame: Often omitted by libraries but used by browsers
- WINDOW_UPDATE behavior: Frequency and use can be telling
- Initial frame combos: Some clients send multiple SETTINGS frames
- TLS fingerprint (JA3): Not part of HTTP/2 but often analyzed together
Why is This a Threat to Scrapers?
Because HTTP/2 fingerprinting dives deep into the protocol layer, it's much harder to fake than User-Agent or JavaScript-based detection. By analyzing the SETTINGS frame, frame order, window updates, and priority frames, servers can accurately determine whether you're using a scraping tool.
Worse yet, detection often happens before your request body is even sent—meaning you could be blocked before sending any data.
HTTP/2 Fingerprinting vs Browser Fingerprinting
Browser fingerprinting uses frontend JavaScript to analyze browser version, plugins, fonts, and more. HTTP/2 fingerprinting, by contrast, focuses on low-level protocol details like SETTINGS frame order, window size, and priority settings. These are tied to the OS, TLS libraries, and kernel-level behavior—making them far more difficult to forge.
As a result, HTTP/2 fingerprinting is more stealthy and harder to bypass than browser fingerprinting.
Can we really bypass it?
Yes! Just learn more from our next 6 methods.
Six Practical Ways to Bypass HTTP/2 Fingerprinting
Method 1: Use a Real Browser to Reproduce Genuine HTTP/2 Behavior
Control a real Chromium browser using Puppeteer or Playwright. Its HTTP/2 stack and TLS handshake inherently mimic human behavior, making it harder to detect.
TLS handshake involves a series of steps allowing the client and server to authenticate and agree on encryption standards before transmitting data.
Recommended setup:
- Use Playwright in headful mode
- Add
--enable-features=NetworkServiceInProcessto enforce native HTTP/2 - Install
puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth - Configure browser environment variables (language, timezone, screen size)
- Rotate IP proxies and User-Agent headers
Pros: Inherently human-like behavior
Cons: High resource consumption, limited scraping throughput
Method 2: Build a Custom HTTP/2 Client that Emulates Browser Behavior
For high concurrency, you can manually construct an HTTP/2 client that mimics browser behavior—from the TLS handshake to initial frame structure.
Key simulation points:
- TLS fingerprint
- ALPN negotiation order
- SETTINGS frame sequence and fields
- Header ordering and case sensitivity
- Proper use of
:authorityandhostheaders
Recommended tools: undici, http2-wrapper, hyper, curl, nghttp2
Pros: High performance, lightweight
Cons: Extremely difficult to implement; requires deep protocol knowledge
Method 3: Use an HTTP/2 Fingerprint Proxy Service
Use a middle-layer proxy that transforms standard requests into ones with browser-like characteristics—for example, TLS-Proxy.
How it works:
- The client sends requests via
httpxor similar - The proxy rewrites HTTP/2 frames and modifies the TLS handshake
- The destination server sees a request mimicking Chrome
Method 4: Replay Real Browser Requests
Export NetLog or capture traffic using Wireshark to log HTTP/2 interactions of a real browser, then replay those sessions.
Recommended tools: nghttp2, h2, chrome://net-export, Wireshark
Pros: Near-perfect emulation of real requests
Cons: Complex process, best suited for small-scale use
Method 5: Match TLS Fingerprints
Before HTTP/2 negotiation, the browser performs a TLS ClientHello handshake that also generates a fingerprint.
Recommended tools:
tls-client(Node.js)uTLS(Go)mitmproxy(Python)
Ensure TLS and ALPN configurations match the target browser for full disguise.
Method 6: Use Nstbrowser Browserless
If you're looking for a stable, efficient, and virtually undetectable scraping solution, Nstbrowser’s Browserless - a cloud browser service is one of the best options available.
Key advantages of Browserless include:
- Real browser environment: Based on Chromium, it simulates genuine user behavior for greater stealth.
- Fingerprint obfuscation: Uses Nstbrowser’s fingerprint library to rotate identities and effectively bypass most anti-bot mechanisms—including TLS and HTTP/2 fingerprinting.
- Cloud-based: No local resources required, supports high-concurrency scraping tasks, easy to integrate and scale.
- Resource monitoring: Real-time tracking of RAM, CPU, and GPU usage ensures efficient load balancing.
- Flexible integration: Supports API, Puppeteer, Playwright, and more—fitting various automation workflows.
Browserless has robust anti-bot and unlocking capabilities built in. It uses real browser fingerprints and human-like behavior to bypass browser-level and HTTP-level detections with ease.
Dig out your free trial now!
The Ending Thoughts
HTTP/2 fingerprinting has become an indispensable next-generation anti-bot technology. Traditional approaches, such as relying solely on user agent spoofing or JavaScript bypasses, are no longer completely effective. To stand out in modern anti-bot systems, the right strategy requires comprehensive emulation - from the protocol stack and TLS to browser behavior.
If you are looking for a high-performance, low-risk bypass solution, Nstbrowser Browserless provides the most human-like emulation capabilities currently available. It is the first choice for data engineers, growth hackers, and security researchers.
More






