Browserless
Browserless: Best AI-Powered Browser to Simplify Your Web Interactions
This article explores the powerful integration of AI agents with Browserless to streamline and enhance web scraping.
Jan 24, 2025Robin Brown
Browser automation and web scraping have become tools for developers, researchers, and enterprise architects. Artificial intelligence (AI) is also transforming these tools and revolutionizing their capabilities, enabling interactive dynamics, intelligent data extraction, and advanced task automation.
AI solutions can adapt to real-time changes, ensuring consistent performance even as websites evolve. This comprehensive guide examines the power of AI agent and Browserless, and explains all the benefits of combining them.
What Is an AI Agent?

AI agents are software systems that use AI technology to autonomously perform tasks or make decisions without direct human intervention. These agents can simulate human-like decision-making processes and adapt to dynamic environments by learning from their experience, interactions, or predefined rules.
They can help you perform specific tasks, answer questions, and automate processes as needed. They can be simple rule-based robots or complex AI systems. AI agents are not autonomous, but can be autonomous if needed. AI autonomous agents can also handle these tasks with very little human intervention.
Types of AI agents
Based on complexity and workflow, the following are the most common types of AI agents:
1. Simple reflex agents
Simple reflex agents operate based on the current input or state of the environment. They follow a set of predefined condition-action rules to decide their responses. These agents react immediately to the conditions they perceive without taking into account past experience.
Example: Basic email spam filters that block certain messages. These filters analyze the content of incoming emails and block those that contain specific keywords or patterns identified as spam.
2. Model-based reflex agents
These agents maintain an internal model of the world, which helps them keep track of the history of events. Unlike simple reflex agents, they can take previous states into account to make better decisions. They update their model based on the feedback received from the environment.
Example: A thermostat that adjusts the temperature. It doesn't just react to the current temperature but also uses previous readings to maintain the desired temperature over time.
3. Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents go a step further than reflex agents by having specific goals. They take actions to achieve a predefined goal and may choose different actions depending on the situation. These agents plan their actions in advance by evaluating possible actions that bring them closer to their objective.
Example: A navigation system that calculates the best route to a destination based on current traffic conditions, roadblocks, and other factors.
4. Utility-based agents
Utility-based agents choose actions based on the concept of utility, which measures how much benefit an action provides toward achieving a goal. These agents evaluate different possible actions based on their outcomes and select the one that maximizes utility or satisfaction.
Example: A shopping recommendation system that suggests products based on the likelihood of purchase, user preferences, and past behavior. It ranks suggestions according to their expected utility to the user.
5. Learning agents
Learning agents can improve their performance over time by learning from their environment and experiences. They use machine learning algorithms to adapt their behavior based on feedback, which helps them make better decisions in the future.
Example: A virtual assistant that learns user preferences over time, such as recognizing frequently asked questions and tailoring responses or actions to better suit the user’s needs.
6. Autonomous agents
Autonomous agents are highly advanced and can make decisions and perform tasks on their own without human intervention. They can adapt to complex environments, plan their own actions, and solve problems in real-time. These agents have a high level of autonomy and intelligence, often combined with advanced AI models.
Example: Autonomous vehicles that navigate roads, recognize obstacles, follow traffic rules, and make driving decisions without human input.
7. Collaborative agents
Collaborative agents are designed to work with other agents (AI or human) to achieve a common goal. These agents share information, coordinate actions, and solve problems together.
They usually communicate with each other to share information/goals, coordinate actions and decisions, and adjust their behavior based on the actions of other agents.
Example: Smart traffic management systems use multiple AI agents to optimize traffic flow. Since there is an agent controlling the traffic lights at each intersection, it can coordinate actions to decide which signal to display.
What Is Browserless?
Browserless is a cloud-based service that lets you run a headless browser without the constraints of a local device. It is designed to enable developers to perform web scraping tasks, automated testing, and other browser-based automation at scale.
As a powerful AI web scraper, Nstbrowser Browserless lets these web agents interact with web-based systems without the need for a full browser interface. For example, you can use Playwright or Puppeteer for test generation or visual analysis. The main benefit is that you can increase the speed of these agents and use fewer resources.
Nevertheless, its ability to understand natural language is what differentiates it from other AI web scraper. Since it can generate human-like responses (both text and voice), it can help you offload tedious tasks. Just like human agents, they can adapt to unexpected situations, such as adding erroneous inputs or using error handling mechanisms.
Since it's omnichannel, it can handle queries across multiple channels (phone, email, chat, etc.) without losing context. All of this happens in real-time — ultimately mimicking normal human interactions.
Why Should We Integrate AI and Browserless?
While AI web scraping tools have demonstrated considerable potential in automating tasks, there are still several technical challenges and obstacles to consider when using AI agents for page interactions:
Dynamic content
Websites today often rely on JavaScript to load data asynchronously, and traditional agents may struggle to capture or interact with elements that only appear after the page has been fully rendered.
Browserless can handle these dynamic pages by running headless browsers that fully render JavaScript, allowing AI agents to interact with elements as a human user would.
Lack of web APIs
Many websites or services do not provide public APIs for easy access to their data. As a result, scraping or automating interactions often requires direct web scraping and dealing with complex HTML structures. This can lead to increased complexity and the need for AI agents to "understand" and navigate websites more intelligently.
By combining AI with Browserless, you can simulate real-user interactions, even when an API is not available. AI can intelligently identify key elements on the page, making it easier for agents to bypass the need for formal APIs and extract or interact with data efficiently. Browserless ensures that these interactions happen without triggering bot detection systems, even in the absence of an API.
Unpredictable Behavior
AI agents, by interacting with third-party systems (like websites, APIs, or other external tools), can encounter situations where the behavior of the system is unpredictable.
You might experience a service outage or a change in your UI, or an API that might have downstream impacts. This becomes a problem when you are running hundreds of tasks at scale, as it can be hard to pinpoint exactly what went wrong.
Let's say you are using an agent to book a flight, and the agent has to handle a new pop-up on the airline’s website that asks for details on vaccine information or a coupon code. If you don’t add the necessary steps in your workflow to handle these pop-ups, the booking might not be made, or you might end up with a booking error.
By integrating AI with Browserless, you can build error-handling mechanisms and fallback solutions. AI can intelligently adapt to changes in the webpage layout, identify new elements (such as pop-ups), and trigger specific actions to handle them. Additionally, Browserless allows running browser instances without a GUI, reducing complexity in identifying and responding to such changes.
Multi-step workflows
Complex workflows often involve multiple steps that span across several systems, each requiring careful coordination and decision-making.
In these cases, maintaining context across various interactions can become challenging, especially when multiple users or systems are involved.
For example, if your agent is helping a user with a mortgage application that needs to pull financial data from multiple systems, the right context and decision flow is needed to make this happen. It might be collecting data through credit checking, underwriting, and your own application system.
Integrating Browserless allows AI agents to execute these workflows in an environment where browser interactions are stable and can be scaled easily, without the risk of errors due to external system changes.
Optimizing Token usage and response time
As the scale of AI usage increases, token usage (in the case of LLMs) and response time can become problematic. As you scale up tasks, each operation might require more resources, increasing the operational cost and response delays.
As web traffic increases, running complex queries across large websites will involve parsing more data, consuming more resources, and increasing response times.
That's why you need to make sure your workflow only contains necessary steps. Here are a few other ways to optimize token usage:
- Cache commonly used information
- Use a layered response system
- Use smaller, task-specific models when appropriate
- Use shorter, more precise prompts
- Request more efficient output formats (bullet points, tables)
How to Achieve AI Web Scraping Using Browserless?
Step1: Preparation
Browserless adopts a browser-centric approach, provides powerful headless deployment capabilities, and ensures higher performance and reliability. For more information about starting with AI web scraping via Browserless, you can get the document to learn more.
Get the API KEY and go to the Browserless menu page of the Nstbrowser client, or you can go to the Nstbrowser client to access
Do you have any wonderful ideas and doubts about web scraping and Browserless?
Let's see what other developers are sharing on Discord and Telegram!
Step2: Confirm crawling target
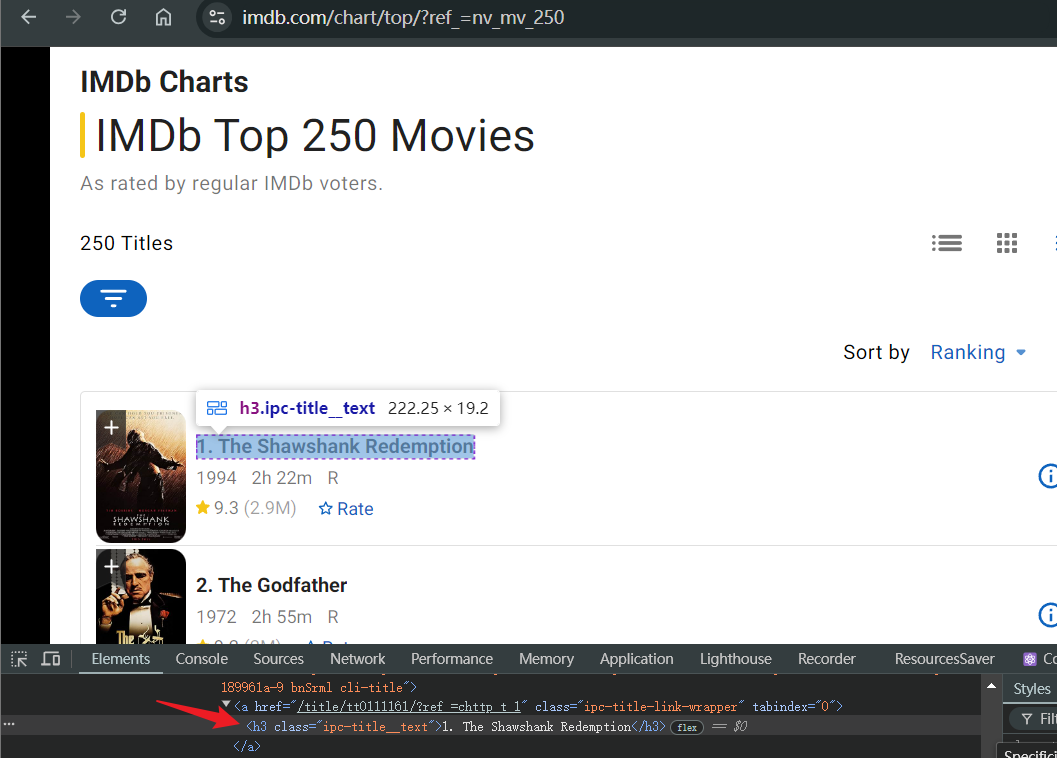
Before we start, we need to make sure what we are going to crawl. In the following example, we try to crawl the movie titles in IMDb's Top 250 Movies. After opening the page:
- Wait for the page to load normally and locate the page to the movie title under IMDb Top 250 Movies
- Open the debug console and identify the html element of the movie title
- Use your favorite library to get the movie title
Step3: Start crawling
Everything is ready, start crawling! We choose to use the powerful Cloud Browserless provided by Nstbrowser to crawl the above content. Below we will list some of the common libraries used together.
Puppeteer
If you haven't chosen a library yet, we highly recommend Puppeteer because it is very active and has many maintainers. It is also built by Chrome developers, so it is one of the highest-quality libraries.
- Install puppeteer-core
Bash
# pnpm
pnpm i puppeteer-core
# yarn
yarn add puppeteer-core
# npm
npm i --save puppeteer-core- Code script
JavaScript
import puppeteer from "puppeteer-core";
const token = "your api key"; // 'your proxy'
const config = {
proxy: 'your proxy', // required; input format: schema://user:password@host:port eg: http://user:password@localhost:8080
// platform: 'windows', // support: windows, mac, linux
// kernel: 'chromium', // only support: chromium
// kernelMilestone: '128', // support: 128
// args: {
// "--proxy-bypass-list": "detect.nstbrowser.io"
// }, // browser args
// fingerprint: {
// userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/128.0.6613.85 Safari/537.36', // userAgent supportted since v0.15.0
// },
};
const query = new URLSearchParams({
token: token, // required
config: JSON.stringify(config),
});
const browserWSEndpoint = `https://less.nstbrowser.io/connect?${query.toString()}`;
// Connect browserless
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint,
defaultViewport: null,
})
console.info('Connected!');
// Create new page
const page = await browser.newPage()
// Visit IMDb top 250 page
await page.goto('https://www.imdb.com/chart/top/?ref_=nv_mv_250')
// Wait for the movie list to load
await page.waitForSelector('.ipc-metadata-list')
// Get a list of movie titles
const moviesList = await page.$$eval('.ipc-metadata-list h3.ipc-title__text', nodes => nodes.map(node => node.textContent));
console.log('[IMDb Top 250 Movies]===>', moviesList);
// Close browser
await browser.close();Congratulation! We have finished our scraping task. You can see the result of 250 movies in the console:
Playwright
- Install Playwright
Bash
pip install pytest-playwright- Code script
Python
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
from urllib.parse import urlencode
import json
token = "your api key" # 'your proxy'
config = {
"proxy": "your proxy", # required; input format: schema://user:password@host:port eg: http://user:password@localhost:8080
# platform: 'windows', // support: windows, mac, linux
# kernel: 'chromium', // only support: chromium
# kernelMilestone: '128', // support: 128
# args: {
# "--proxy-bypass-list": "detect.nstbrowser.io"
# }, // browser args
# fingerprint: {
# userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/128.0.6613.85 Safari/537.36', // userAgent supportted since v0.15.0
# },
}
query = urlencode({"token": token, "config": json.dumps(config)})
browser_ws_endpoint = f"ws://less.nstbrowser.io/connect?{query}"
def scrape_imdb_top_250():
with sync_playwright() as p:
# Connect browserless
browser = p.chromium.connect_over_cdp(browser_ws_endpoint)
print("Connected!")
# Create new page
page = browser.new_page()
# Visit IMDb top 250 page
page.goto("https://www.imdb.com/chart/top/?ref_=nv_mv_250")
# Wait for movie list to load
page.wait_for_selector(".ipc-metadata-list")
# Get a list of movie titles
movies_list = page.eval_on_selector_all(
".ipc-metadata-list h3.ipc-title__text",
"nodes => nodes.map(node => node.textContent)",
)
print("[IMDb Top 250 Movies]===>", movies_list)
# Close browser
browser.close()
scrape_imdb_top_250()Of course, the following is the scraping result:

Select your favorite language and library, execute the corresponding script, and you can see the crawled results!
3 Hot technology trends
1. Generative AI:
- Generative AI will empower automation technology, enabling AI to generate more complex and personalized operation strategies, thereby improving the intelligence of automated tasks.
- AI can generate the most appropriate interaction solutions based on web content and user behavior, and automatically adapt to different types of anti-crawler technologies and dynamic pages.
2. LLMs (GPT, ClaudeAI, etc.)
- Large language models can enable AI Agents to understand and operate more complex web elements when performing tasks, including extracting information and analyzing web content, through natural language processing technology.
- By integrating LLM, AI Agents can perform language understanding, information extraction, and analytical decision-making when performing automated tasks, improving the flexibility and intelligence of tasks.
3. Behavior Simulation
- Behavior simulation technology enables AI to accurately simulate the interactive behavior of real users, improve concealment and bypass detection systems.
- AI can simulate each user's unique behavior patterns, including mouse movements, click habits, and browser settings, to prevent being identified as machine operations.
AI Agent and Browserless — Simplifies Your Web Automation
You have fully understood the entire content of AI agent. The combination of AI agent and Browserless will bring comprehensive intelligence to web page operations.
From bypassing anti-crawler to simulating complex user behaviors, to the future fully automated web page operation platform, AI and Browserless will become the core of intelligent web page interaction.
More






